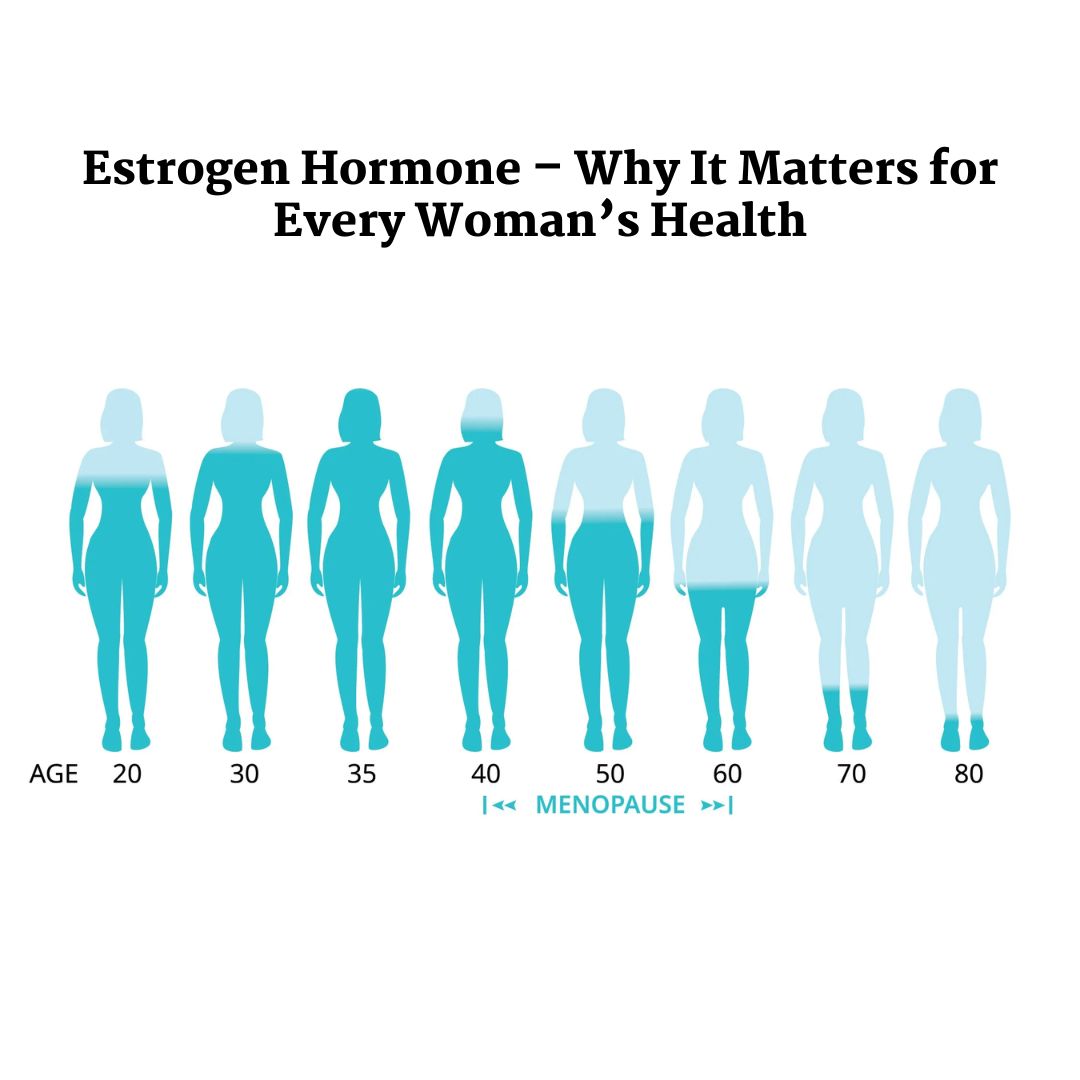
The estrogen hormone in females is often described as the “female hormone,” but its functions go far beyond periods and pregnancy. In fact, estrogen is a master regulator in the body, affecting your heart, bones, mood, brain, and even your skin. Whether you are in your teenage years, trying to conceive, or navigating menopause, balanced estrogen levels are essential for good health.
Unfortunately, hormonal imbalances are becoming increasingly common. Many women struggle with low estrogen levels or high estrogen dominance without even realizing it. Symptoms like fatigue, irregular cycles, mood swings, or poor sleep are often brushed aside. However, they could be signs that the estrogen hormone in females needs attention.
This detailed guide explains what estrogen is, how it works, symptoms of imbalance, and ways to naturally support healthy levels.
1. What Is the Estrogen Hormone in Females?
The estrogen hormone in females is a group of steroid hormones responsible for the development and regulation of the reproductive system and secondary sexual characteristics. While it is present in men in smaller amounts, it plays a much larger role in women.
The ovaries are the primary producers of estrogen, although small amounts are also produced by the adrenal glands and fat tissue.
Key Functions of the Estrogen Hormone in Females
-
Regulating the menstrual cycle and ovulation
-
Preparing the uterus lining for implantation
-
Maintaining bone strength and density
-
Supporting healthy cholesterol levels and heart function
-
Keeping the skin hydrated and elastic
-
Influencing mood, memory, and brain health
-
Supporting vaginal health
Because estrogen affects multiple systems in the body, even a slight imbalance can lead to a range of symptoms.
2. The Different Types of Estrogen Hormone in Females
There are three main forms of the estrogen hormone in females:
-
Estradiol (E2): The most active form, produced during reproductive years.
-
Estrone (E1): Produced after menopause, mainly in fat tissue.
-
Estriol (E3): Produced in large amounts during pregnancy.
Doctors often measure these levels to understand where you are in your hormonal life stage. As a result, they can diagnose imbalances more accurately.
3. Signs and Symptoms of Low Estrogen Hormone in Females
Estrogen naturally fluctuates during your monthly cycle and across life stages. However, chronically low estrogen levels can cause serious issues.
Common Causes
-
Perimenopause and menopause
-
Over-exercising or extreme dieting
-
Chronic stress
-
Certain autoimmune conditions
-
Premature ovarian failure
-
PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome)
Symptoms of Low Estrogen
-
Irregular or missed periods
-
Hot flashes or night sweats
-
Vaginal dryness or discomfort
-
Low libido
-
Pain during intercourse
-
Weak bones or frequent fractures
-
Fatigue or brain fog
-
Mood changes like depression or anxiety
4. Symptoms of High Estrogen Hormone in Females (Estrogen Dominance)
On the other hand, having too much estrogen can also be harmful. This is often referred to as estrogen dominance.
Possible Causes
-
Obesity (fat cells produce extra estrogen)
-
Hormone replacement therapy or birth control
-
Liver dysfunction (affects hormone clearance)
-
Environmental xenoestrogens (plastics, pesticides)
Symptoms of High Estrogen
-
Heavy or painful periods
-
Breast tenderness or swelling
-
Weight gain around hips and waist
-
Bloating and water retention
-
Mood swings and irritability
-
Hair thinning
5. Why Estrogen Hormone Imbalance in Females Should Not Be Ignored
The estrogen hormone in females plays a protective role in women’s health. Consequently, when levels are off, it can lead to long-term risks:
-
Bone loss (osteoporosis)
-
Heart disease due to cholesterol changes
-
Infertility from irregular ovulation
-
Mood disorders including anxiety and depression
Early diagnosis and support can make a significant difference.
6. How to Maintain Healthy Estrogen Hormone in Females
A. Support Through Diet
To begin with, include phytoestrogen-rich foods like flaxseeds, chickpeas, soy, and lentils. Moreover, eat cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cabbage, kale) which help metabolize excess estrogen. Choosing whole grains and fiber-rich foods can regulate hormone detoxification. In addition, maintain healthy fats (avocado, olive oil, nuts) for hormone production.
B. Exercise in Moderation
Regular exercise helps manage weight and hormone balance. However, avoid over-exercising, which can reduce estrogen levels.
C. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can suppress the ovaries and lower estrogen. Therefore, practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing are highly beneficial.
D. Minimize Toxin Exposure
Avoid BPA-containing plastics and choose organic produce when possible. As a result, you can reduce exposure to synthetic chemicals that mimic estrogen in the body.
7. Medical Treatments for Estrogen Hormone Imbalance in Females
If your doctor diagnoses significantly low estrogen levels, they may suggest hormone therapy.
Estradiol therapy is the most common treatment. It can be prescribed in the form of:
-
Estradiol gels or creams
-
Oral tablets
-
Patches or injections
This therapy can reduce symptoms like hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and bone loss. Nevertheless, it must be done under medical supervision to avoid side effects.
8. Estrogen Hormone in Females Across Life Stages
A. Teens and Young Women
Estrogen drives puberty, regulates cycles, and supports reproductive health. For example, PCOS can disrupt these levels early.
B. Reproductive Years
Balanced estrogen is key for fertility and preparing the uterine lining for pregnancy.
C. Perimenopause and Menopause
Estrogen production declines, leading to symptoms like hot flashes, bone loss, and vaginal discomfort.
9. When Should You Get Tested for Estrogen Hormone in Females?
You should ask your doctor for an estrogen hormone test if you experience:
-
Missed or irregular cycles
-
Hot flashes or excessive sweating
-
Unexplained weight gain or bloating
-
Mood changes
-
Difficulty conceiving
A simple blood test can check your estradiol, estrone, and estriol levels.
10. Key Takeaways on Estrogen Hormone in Females
-
The estrogen hormone in females is essential for heart, bones, brain, and reproductive health.
-
Symptoms of low or high estrogen should not be ignored.
-
Diet, exercise, and stress management can help maintain balance naturally.
-
Hormone therapy may be prescribed when needed — but always under medical supervision.
Final Word from Quinek Life Sciences
At Quinek Life Sciences, we believe that women’s health begins with awareness. The estrogen hormone in females is a cornerstone of female wellbeing, yet it is often overlooked until symptoms become severe.
If you are experiencing any signs of hormonal imbalance, don’t delay. Speak to your doctor and request a hormonal health evaluation. Ultimately, early intervention can prevent serious health issues and improve your quality of life.
Healthy hormones mean a healthier you.